As a business analyst, one of the fundamental tools you need to understand and utilize is Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). Think of BPMN as your trusty map that helps you navigate the intricate world of business processes. Just as a map guides travelers through unfamiliar terrain, BPMN provides a visual representation of how various activities, systems, and stakeholders interact within a business environment. By using BPMN, you can improve communication, streamline processes, and ultimately drive organizational success.
Understanding Business Process Model and Notation
Before delving into the intricacies of BPMN, let’s establish a solid foundation by understanding its definition and purpose. BPMN, as its name suggests, is a modeling notation used to represent and document business processes. It provides a standardized language that allows business analysts, stakeholders, and technical teams to collaborate effectively in analyzing, designing, and optimizing processes.
But what exactly does BPMN entail? How does it bridge the gap between business and IT? Let’s explore further.
Definition and Purpose of BPMN
At its core, BPMN serves as a bridge between business and IT, translating complex processes into visual diagrams that are easily comprehensible. Just as a translator helps people communicate across language barriers, BPMN acts as a common language that breaks down the communication barriers between business and IT professionals.
Imagine a scenario where a business analyst needs to explain a complex process to a software developer. Without a common language, misinterpretations and misunderstandings can easily occur. BPMN provides a visual representation of the process, making it easier for both parties to understand and collaborate effectively.
But why is this important? The purpose of BPMN is to capture and communicate all aspects of a business process comprehensively. It allows you to map out the sequence of activities, decisions, and interactions that occur within a process. This visual representation helps stakeholders gain a clear understanding of the process, identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and collaboratively optimize it for better results.
By using BPMN, organizations can streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Key Components of BPMN
BPMN diagrams consist of various essential components that work together to create a holistic view of a process. Like puzzle pieces that fit together to form a complete picture, these components interact to represent the flow and structure of a business process.
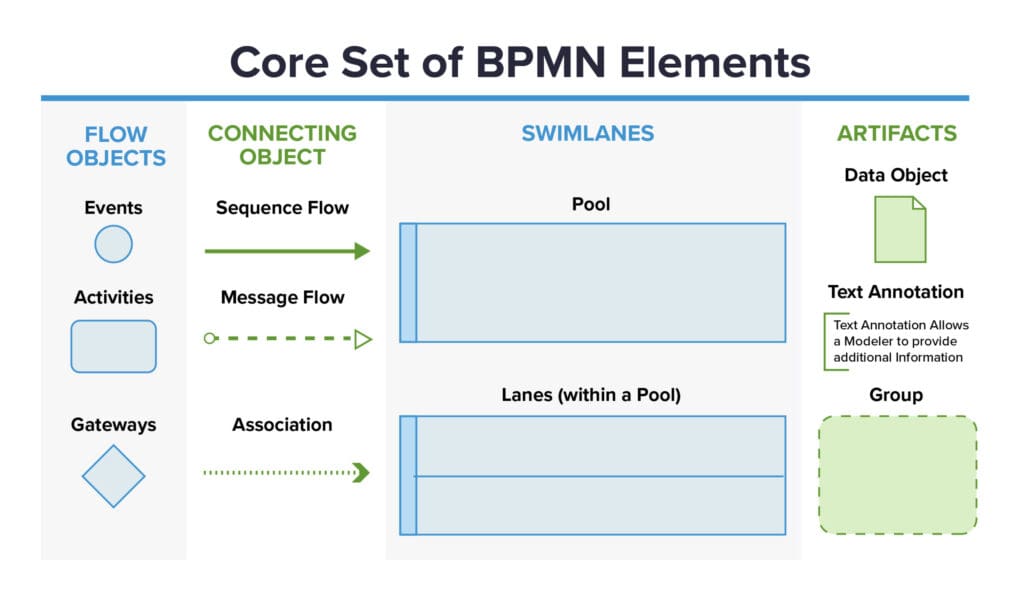
Let’s take a closer look at the key components in BPMN:
- Flow Objects: These represent the individual activities, events, or gateways that make up a process. They are the building blocks of a BPMN diagram, capturing the specific actions or decisions that occur within a process. Examples of flow objects include tasks, subprocesses, events, and gateways. Each flow object has its own unique characteristics and symbols, allowing for clear representation and understanding.
- Connecting Objects: These establish the flow and relationships between the flow objects. They represent the sequence of activities, decisions, or events within a process. Connecting objects include sequence flows, message flows, and associations. These objects ensure that the process flows smoothly from one activity to another, providing a clear path for stakeholders to follow.
- Swimlanes: These visually separate the process activities based on the roles of participants or functional areas. Swimlanes provide a clear structure to the BPMN diagram, allowing stakeholders to identify which activities belong to specific departments, teams, or individuals. This segregation helps in understanding the responsibilities and interactions between different stakeholders, ensuring a comprehensive view of the process.
- Artifacts: These provide additional information or context to the process, such as data objects or annotations. Artifacts help in adding more details and clarity to the BPMN diagram. They can include data objects, groups, and annotations. Data objects represent the information that is used or produced by the process, while groups help in organizing related activities or objects. Annotations provide explanatory notes or comments, making the diagram more informative and understandable.
By utilizing these key components, BPMN diagrams provide a comprehensive and detailed representation of business processes. They enable stakeholders to visualize the flow, understand the roles and responsibilities of participants, and identify potential areas for improvement.
As organizations continue to embrace BPMN, the language of business process modeling becomes more standardized and accessible. This allows for effective collaboration, analysis, and optimization of processes, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and better business outcomes.
The Role of BPMN in Business Analysis
Now that we have a solid understanding of BPMN, let’s explore its importance in the realm of business analysis. Think of BPMN as your analytical lens, enabling you to view and analyze complex business processes from a bird’s-eye perspective, while also zooming in to gain a granular understanding of specific activities.
Enhancing Communication through BPMN
Clear communication is the foundation of successful business analysis. Like a skilled translator, BPMN ensures that all stakeholders have a common understanding of a process, no matter their backgrounds or areas of expertise. By providing a visual representation of a process that is easy to interpret and discuss, BPMN fosters effective communication among teams and prevents misunderstandings that may otherwise lead to costly errors or delays.
Streamlining Business Processes with BPMN
Streamlining business processes is not unlike untangling a tangled web. BPMN acts as your trusty toolset, enabling you to dissect and optimize processes for maximum efficiency. By analyzing the visual representation of a process in BPMN, you can identify redundancies, bottlenecks, or unnecessary complexities that may impede productivity.
Once these areas for improvement are identified, you can collaborate with stakeholders, propose alternative process designs, and optimize the flow, ultimately resulting in faster, smoother, and more cost-effective operations.
Different Types of BPMN Diagrams
As a business analyst, your toolset is not limited to a single type of BPMN diagram. Just as a diverse range of tools is essential for different tasks, various BPMN diagram types can be used to tackle different business analysis challenges.
Process Diagrams
Process diagrams are the bread and butter of BPMN. Picture them as the foundation of your analytical toolkit. These diagrams depict the sequence and flow of activities within a single process. With process diagrams, you can visualize how tasks are interconnected, decision points, and the overall flow from start to finish. They serve as a powerful means of capturing, analyzing, and communicating the structure and behavior of a process.
Collaboration Diagrams
In business analysis, collaboration is key. Collaboration diagrams, also known as choreography diagrams, help you visualize how multiple participants interact within a process. Just as synchronized dancers gracefully move together, collaboration diagrams show the flow of messages, triggers, and responses exchanged between participants. This type of diagram is particularly useful in capturing complex interactions and dependencies between different stakeholders or systems involved in a process.
Advantages of Using BPMN in Business Analysis
Now that we’ve explored the various components and diagram types in BPMN, let’s take a closer look at the advantages it offers in the realm of business analysis.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Time is a precious resource in the business landscape. Just as a well-organized toolbox helps you complete tasks more efficiently, BPMN empowers you to identify inefficiencies and optimize processes, leading to improved efficiency and productivity. By visualizing the process flow and identifying areas for improvement, stakeholders can make informed decisions, streamline operations, and allocate resources effectively.
Enhanced Visibility and Control
Imagine driving through a foggy landscape without headlights. It would be challenging to navigate safely and make informed decisions. Similarly, BPMN brings clarity and visibility to business processes. By providing a visual framework, BPMN allows stakeholders to have a clear understanding of how processes operate, fostering informed decision-making, and granting greater control over operations. This enhanced visibility leads to better risk management, identification of compliance gaps, and the ability to adapt to changing business environments swiftly.
Challenges in Implementing BPMN
While the benefits of BPMN are substantial, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that may arise during its implementation. Like any new tool or skill, BPMN requires investment in time and resources to fully reap its rewards.
Training and Skill Requirements
Implementing BPMN requires not only a foundational understanding of the notation itself but also the ability to apply it effectively. Just as mastering a foreign language takes time and practice, becoming proficient in BPMN requires training and skill development. Business analysts and other stakeholders need to invest time in learning the intricacies of BPMN and how to apply it to real-world scenarios. Organizations must allocate resources for training programs and ensure ongoing skill development to maximize the benefits of BPMN.
Potential Complexity in Large Businesses
Large organizations often have complex and interconnected processes. Trying to capture and model these processes using BPMN can be likened to solving a vast puzzle. The challenge lies in balancing the level of detail required for comprehension without overwhelming stakeholders with complexity. To mitigate this challenge, it is crucial to adopt a phased approach, starting with high-level process modeling and gradually drilling down into specific areas as required. By breaking down the complexity into manageable chunks, organizations can successfully leverage BPMN to analyze and optimize their business processes.
In conclusion, Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a powerful tool in the business analyst‘s toolkit, enabling effective communication, streamlined processes, and improved efficiency. Like a skilled translator, BPMN bridges the gap between business and IT, facilitating collaboration and understanding. By utilizing different types of BPMN diagrams and leveraging its advantages, organizations can navigate the complexities of their business processes with confidence. While challenges may arise, such as training requirements and managing complexity, with the right approach and investment, the rewards afforded by BPMN are well worth the effort.

